What is RFP; How to Write, Manage, and Win Proposals?
In today’s fast-paced and ever-evolving business landscape, Request for Proposals (RFPs) serve as more than just a means to solicit bids—they’re a vital component of strategic decision-making, vendor partnerships, and project success. Whether you’re a startup looking for marketing services or a large corporation planning a multimillion-dollar IT infrastructure upgrade, RFPs are your blueprint for finding the right solution and partner.
At their core, RFPs streamline vendor selection, procurement, and project planning, ensuring that companies don’t just get the job done, but get it done right. The process fosters competitive bidding, cost efficiency, and quality assurance—three pillars of successful procurement. Companies issuing RFPs can compare proposals side by side, assess different approaches, and ensure they’re getting the best value for their investment.
The Growing Importance of RFPs in Emerging Industries
As per the data from Economic Times, industries across the globe—including technology, construction, and AI development—are increasingly relying on RFPs to make critical decisions. AI-powered foundation models, for example, have become a hot topic as governments and private enterprises seek vendors to build next-generation solutions. This growth is a testament to how RFPs are no longer limited to traditional sectors like construction and government but have become key players in tech-driven and innovation-centric industries.
Gaining a Competitive Edge
Mastering the RFP process means you’re not only choosing the right vendors but also saving time, money, and effort. Businesses that understand and effectively use RFPs can negotiate better deals, secure higher-quality services, and minimize project risks. In fact, companies leveraging AI-enhanced RFP tools have seen improved proposal accuracy, streamlined collaboration, and faster procurement cycles according to the data discussed in IDC Blogs.
This guide will help you demystify the entire RFP process—from writing an effective proposal to evaluating and selecting vendors. Whether you’re responsible for creating one or responding to one, understanding RFPs can significantly boost your company’s operational efficiency and overall success. So, buckle up as we explore the ins and outs of RFPs and how they can elevate your business to the next level.
What Is an RFP (Request for Proposal)?
An RFP (Request for Proposal) is a formal document issued by organizations to solicit bids or proposals from potential vendors or service providers, rightly mentioned in Wikipedia. The purpose of the RFP is to clearly define project requirements and establish evaluation criteria to ensure that businesses choose the most suitable partner. It acts as a bridge between buyers and vendors, streamlining the selection process while promoting transparency and competitive bidding.
Unlike a simple inquiry or quote request, an RFP typically asks for detailed proposals explaining how a vendor intends to address a project’s unique needs, timelines, and budgetary constraints.
Purpose of an RFP
The primary goal of an RFP is to identify the right partner who can deliver tailored, high-quality solutions within the defined scope and budget. Organizations issue RFPs for a variety of reasons, such as:
- To explore innovative vendor approaches to solving business challenges
- To ensure fair competition by inviting multiple proposals
- To obtain cost-effective solutions without compromising quality
Businesses often issue RFPs when they need solutions that go beyond off-the-shelf products. For example, in large-scale IT system implementations or marketing campaigns, vendors are asked to present customized proposals addressing unique requirements.
Industries Using RFPs
RFPs have become essential across a broad range of industries where tailored solutions, competitive bidding, and vendor accountability are critical. Some common industries using RFPs include:
- Construction and Real Estate: To secure contracts for large infrastructure projects like roads, buildings, and public utilities.
- Information Technology (IT): For software development, cloud migrations, and cybersecurity solutions.
- Government Procurement: Government agencies frequently issue RFPs to ensure fair bidding processes for public sector projects.
- Marketing and Creative Services: To source advertising agencies, branding consultants, and digital marketing vendors.
For instance, the Indian government recently issued an RFP for developing a local language AI foundation model to bolster AI innovation, emphasizing the increasing reliance on RFPs even in emerging tech sectors. As per the Economic Times, this project highlights how RFPs are critical not only in traditional fields like construction but also in cutting-edge fields like artificial intelligence.
Key Components of an RFP Document
Creating a well-structured Request for Proposal (RFP) is crucial to ensure you attract high-quality vendors who understand your needs and can deliver exceptional results. A comprehensive RFP document should include the following essential components:
1. Project Overview
The project overview serves as an introduction, outlining the project’s objectives, purpose, and high-level goals. It should provide vendors with enough context to understand the company’s vision and what success looks like. For example, if the RFP is for a software implementation project, the overview should explain the current challenges, desired outcomes, and how the project aligns with the company’s long-term strategy.
Tip: Be concise but informative. Providing relevant background information will help vendors craft more targeted proposals.
2. Scope of Work (SOW)
The Scope of Work (SOW) is the crux of the RFP. It defines the deliverables, tasks, milestones, and timelines that the vendor must adhere to. This section should specify what work needs to be done, who will be responsible for each task, and key deadlines.
Details to Include:
- Project phases or stages (e.g., discovery, implementation, testing, and delivery)
- Expected milestones and key performance indicators (KPIs)
- Any specific tools, technologies, or methodologies to be used
By clearly defining expectations, you minimize the risk of misunderstandings and ensure that vendors can provide accurate cost and time estimates.
3. Evaluation Criteria
This section tells vendors how their proposals will be assessed and which aspects are most important to the decision-making process. Common evaluation factors include:
- Pricing and cost-effectiveness
- Technical expertise and industry experience
- Proven track record with similar projects
- Proposed methodology or approach
- Post-project support and maintenance options
You can assign weights to different criteria to prioritize what matters most to your project. For example, in a software development project, you might prioritize technical expertise over cost if innovation is critical.
4. Submission Requirements
To maintain consistency and simplify the review process, clearly outline the submission guidelines and requirements that vendors must follow. Include instructions on:
- Proposal format and structure: Specify if you require sections such as an executive summary, technical approach, and pricing breakdown.
- Deadline for submission: Clearly state the due date and time, along with timezone information.
- Required documents: Highlight any additional materials needed, such as case studies, references, or certifications.
- Submission method: Specify whether proposals should be submitted via email, an online portal, or physical delivery.
Setting clear submission requirements ensures that you receive proposals in a consistent format, making it easier to compare vendors.
5. Terms and Conditions
This section outlines the legal and contractual obligations vendors must agree to if selected. It may cover topics such as:
- Payment terms: Milestone-based payments, upfront costs, or installments
- Contract duration: Length of the project and possible extensions
- Liabilities and penalties: Consequences of missed deadlines or non-compliance
- Confidentiality and intellectual property rights: Protect sensitive information and establish ownership of deliverables
Including terms and conditions ensures that all parties are aligned on the legal framework governing the project, reducing the risk of disputes during or after execution.
How Does the RFP Process Work?
The RFP (Request for Proposal) process is a structured approach designed to help businesses find the best vendor to meet their project needs. By following specific phases, organizations can ensure that their proposals are competitive, comprehensive, and meet client expectations. Here’s a breakdown of the key phases in the RFP process:
Explore comprehensive steps to prepare an RFP.
Phase 1: Evaluate
The first step in the RFP process is to evaluate whether the opportunity aligns with your organization’s capabilities and strategic goals. Not every RFP is worth pursuing, so businesses must critically assess whether they have the resources and expertise to deliver the project successfully.
Key Tasks:
- Review the RFP: Examine the document thoroughly to understand the client’s requirements, scope of work, and expectations.
- Assess Profitability: Determine if the project is financially viable and aligns with long-term growth objectives.
- Ask Critical Questions: Are you capable of meeting the requirements? Can you deliver within the specified timeframe and budget?
Outcome: Only move forward if the opportunity is realistic and offers strategic value.
Phase 2: Research
Once you decide to proceed, the next phase involves researching the client’s business, challenges, and competitors. This is critical to developing a tailored proposal that addresses the client’s specific needs.
Key Tasks:
- Understand the Client: Conduct research on the organization’s history, industry, and pain points. Identify any past projects that may provide insights into their expectations.
- Analyze Competitors: Understand who you’re competing against and what differentiates them. This helps you position your proposal more effectively.
- Gather Internal Expertise: Consult team members who have experience with similar projects to gather useful insights.
Pro Tip: Leveraging internal knowledge can help you create a proposal that highlights your strengths and offers unique solutions.
Phase 3: Plan
With sufficient research in hand, it’s time to develop a response strategy and outline the proposal structure. Planning ensures that all team members are aligned and aware of their roles.
Key Tasks:
- Set Clear Objectives: Identify what you aim to achieve with the proposal, such as highlighting cost efficiency, technical expertise, or innovative approaches.
- Create a Timeline: Break down tasks with deadlines for each section of the proposal. This ensures you stay on track and meet submission deadlines.
- Assign Roles: Assign specific sections to team members, such as the executive summary, technical details, and cost estimates.
Tip: Conduct a kickoff meeting to ensure everyone understands their responsibilities and the overall strategy.
Phase 4: Draft
In this phase, you begin drafting the proposal by personalizing responses and highlighting your organization’s strengths. Ensure that each section addresses the client’s key concerns and outlines how you’ll solve their problem.
Key Tasks:
- Tailor Your Responses: Avoid generic responses. Use insights from the research phase to demonstrate that you understand the client’s challenges and can provide customized solutions.
- Highlight Strengths: Emphasize unique value propositions, such as innovative approaches, industry expertise, or past successes.
- Include Case Studies: Support your claims with real-world examples of similar projects you’ve completed successfully.
Tip: Collaborate with subject matter experts (SMEs) to provide detailed and accurate responses for technical sections.
Phase 5: Respond
The final phase focuses on reviewing, finalizing, and submitting the proposal. This step ensures that your submission is error-free, meets all requirements, and leaves a strong impression.
Key Tasks:
- Conduct a Final Review: Double-check that all required sections are complete and adhere to the RFP guidelines. Look for any inconsistencies, errors, or missing information.
- Proofread the Proposal: Ensure that the content is clear, concise, and free from grammatical errors.
- Check Submission Requirements: Confirm the submission method (e.g., email, online portal) and ensure that you meet the deadline.
- Save and Repurpose Content: Store key sections of the proposal in a content library for future use, making it easier to respond to similar RFPs in the future.
AI-Enhanced RFPs: A Game Changer
As AI-powered tools become increasingly common in managing RFP processes, businesses can significantly reduce manual workloads, improve collaboration, and enhance proposal quality. As per the data from IDC Blogs, AI tools can help automate responses, ensure compliance with client requirements, and generate content recommendations based on past submissions. This not only streamlines the entire process but also improves the chances of winning contracts by delivering more polished and targeted proposals.
By following these structured phases, businesses can ensure that their proposals are well-organized, comprehensive, and tailored to the client’s specific needs—ultimately increasing their chances of success.
Benefits of an RFP
An RFP (Request for Proposal) is more than a procurement document—it’s a strategic tool that can unlock several advantages for businesses by ensuring they select the most suitable vendors while optimizing project outcomes.
1. Competitive Pricing
An RFP encourages vendors to submit their best offers in a competitive environment. By soliciting multiple bids, businesses can evaluate different pricing models and options, ensuring they receive cost-effective solutions. This competitive bidding process often leads to significant cost savings without compromising on quality.
2. Quality Assurance
RFPs outline clear specifications, requirements, and expectations, helping businesses ensure that only qualified vendors submit proposals. By including evaluation criteria that emphasize experience, technical expertise, and proven performance, companies can select vendors who meet or exceed quality benchmarks. This leads to better project outcomes and reduced rework.
3. Transparency
A well-structured RFP promotes fairness and transparency throughout the procurement process. By documenting every step—such as criteria for evaluation, timelines, and deliverables—organizations can maintain accountability and ensure that the selection process is auditable. This transparency is particularly important in government and public sector projects where fair competition is mandated.
4. Minimized Risk
By setting clear expectations and project requirements upfront, RFPs help businesses mitigate risks associated with cost overruns, delays, or substandard deliverables. Companies can identify potential risks early during vendor evaluation and include contingencies to address them.
5. Real-World Example
India’s government recently issued an RFP for developing local language AI foundation models to ensure high data accuracy and minimize risks associated with handling multilingual datasets. As per the data from Economic Times, this strategic approach ensures better project outcomes through detailed requirement setting.
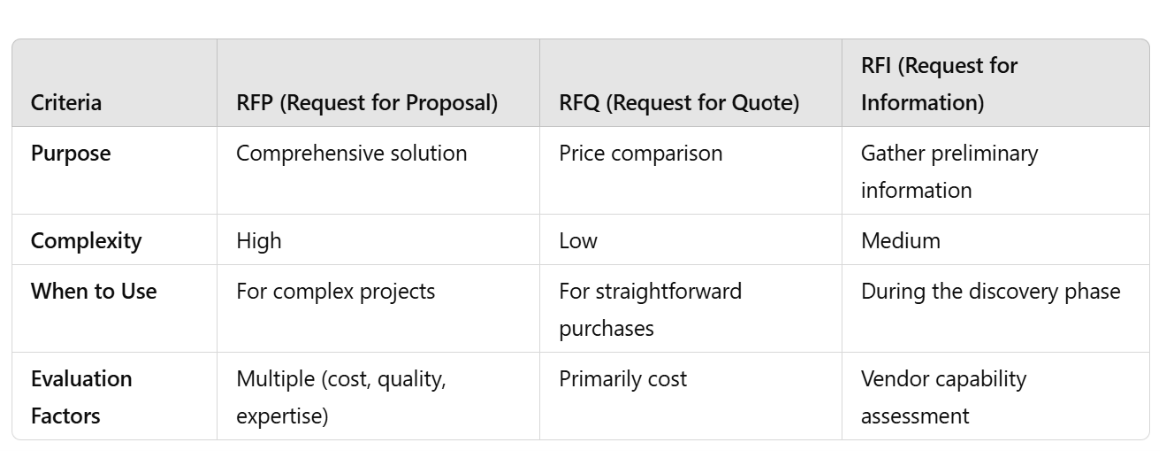
RFP vs. RFQ vs. RFI: A Quick Comparison
Key Difference: An RFP helps businesses source the right vendor by requesting detailed proposals, whereas an RFQ focuses on pricing alone, and an RFI is primarily used during the discovery phase to gather vendor information.
Understand the differences between RFPs, RFQs, and RFIs.
Real-World Examples of Successful RFPs
A large tech company recently utilized AI-based RFP automation to reduce their procurement cycle time by 30% while increasing vendor diversity. These examples highlight the importance of leveraging advanced tools in today’s competitive landscape.
By using automated workflows and content centralization, they streamlined the proposal evaluation process and ensured compliance with their selection criteria.
Such examples highlight the importance of incorporating advanced RFP platforms in today’s competitive procurement landscape. By doing so, businesses not only save time but also improve the quality of vendor selection, ultimately driving better project outcomes.
Conclusion: Master the Art of RFPs
Mastering the RFP process is a game-changer for businesses seeking to gain a competitive edge in today’s dynamic markets. From understanding the differences between RFPs, RFQs, and RFIs to leveraging AI-driven tools that improve speed and accuracy, adapting to modern trends and best practices is critical. Whether you’re in tech, construction, or marketing, knowing how to craft, manage, and respond to effective RFPs will set you apart and enhance organizational success.
Start Your RFP Optimization Journey
Ready to elevate your procurement game? Leverage the power of AI and automation tools to stay ahead of the curve. Sign up at GetGenerative.ai to unlock powerful, next-gen AI-based solutions that can simplify your proposal writing and evaluation processes.
What You’ll Get with GetGenerative.ai
- Easy RFP Generation: Generate high-quality RFP responses and proposals within minutes using AI-powered templates.
- Seamless Team Collaboration: Work together with team members and stakeholders in real time, ensuring faster feedback and approvals.
- AI-Driven Insights: Receive intelligent recommendations designed to enhance proposal quality and boost your chances of success.
💡 Pro Tip: As procurement processes evolve, embracing AI tools and innovative practices will help you navigate complexities, ensuring that you remain competitive and secure the best possible project outcomes.
Don’t wait! Sign in now and begin transforming your RFP processes today—the future of efficient procurement depends on the strategies you implement today.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the RFP process?
The RFP process is structured to respond to Requests for Proposals, ensuring thorough, competitive, and client-aligned proposals.
2. What are the 5 phases of the RFP process?
The five phases are Evaluate, Research, Plan, Draft, and Respond.
3. Why is an RFP process checklist important?
An RFP process checklist helps streamline tasks, track progress, and ensure no missed steps, leading to a timely and effective response.
4. What common pitfalls should I avoid in the RFP process?
Avoid bidding on unwinnable opportunities, missing important details, and lack of team preparation.
5. How can an RFP platform help?
An RFP platform centralizes content management, enhances collaboration, automates responses, tracks progress, and ensures compliance with RFP requirements.