Generative AI vs. Predictive AI: What’s the Difference?
AI has revolutionized how we interact with technology, particularly through its two distinct subsets: generative AI and predictive AI. While these technologies share a foundation in machine learning, their purposes and applications vary significantly.
In this blog, we’ll explore what sets generative AI apart from predictive AI, how they work, and the unique use cases they serve.
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI refers to artificial intelligence that produces new content—text, images, audio, video, or code—based on a user’s input. It’s like a digital artist or writer that can create something entirely new from scratch, inspired by its training data.
How Generative AI Works
Generative AI relies on models trained with vast amounts of data to identify patterns and relationships. These models include:
- Transformer Models: Use attention mechanisms to process sequences of data efficiently.
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): Two networks work together, one generating content and the other evaluating its quality.
- Variational Autoencoders (VAEs): Learn compact data representations to create variations.
- Diffusion Models: Gradually refine noisy data into recognizable content.
Applications of Generative AI
Generative AI finds use across various industries:
- Content Development: Producing written content, visual art, or musical compositions.
- Medical Training: Generating synthetic healthcare data for educational and testing purposes.
- Entertainment Design: Crafting lifelike virtual settings and dynamic characters.
- Tech Support: Enhancing coding efficiency through automated code creation and error resolution.
Advantages of Generative AI
- Accelerates content production.
- Facilitates creative brainstorming.
- Enhances personalization.
Challenges of Generative AI
- Prone to hallucinations or inaccuracies.
- Risk of plagiarism and copyright infringement.
- Security concerns regarding sensitive data.
Related Read – Generative AI Roadmap For Absolute Beginners
What is Predictive AI?
Predictive AI focuses on forecasting future outcomes or trends using historical data. Think of it as a crystal ball for businesses, providing actionable insights.
How Predictive AI Works
Predictive AI uses machine learning and statistical models to analyze data and predict potential outcomes. Key techniques include:
- Regression Analysis: Establishing relationships between variables.
- Time Series Analysis: Studying patterns over time to make forecasts.
- Clustering: Grouping data points based on similarities.
Applications of Predictive AI
Predictive AI’s strength lies in decision-making:
- Financial Forecasting: Predicting stock trends and market behavior.
- Fraud Detection: Identifying unusual patterns in transactions.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Anticipating demand to streamline logistics.
- Healthcare: Early diagnosis through pattern recognition.
Advantages of Predictive AI
- Provides actionable insights for informed decisions.
- Enhances efficiency in resource planning.
- Improves accuracy in identifying future trends.
Challenges of Predictive AI
- Requires high-quality, bias-free data.
- Lacks absolute certainty in predictions.
- Relies heavily on human interpretation of results.
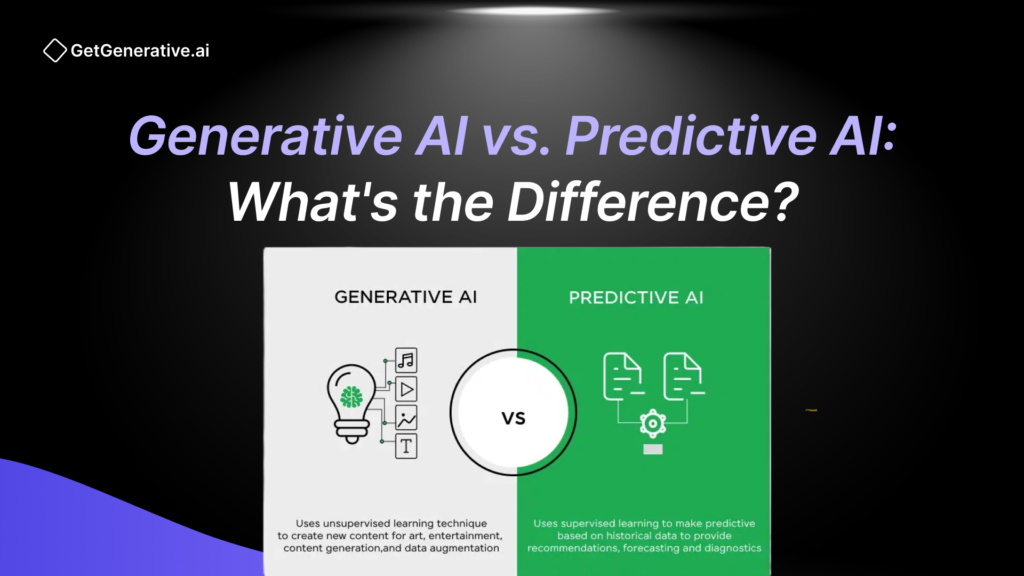
Generative AI vs. Predictive AI
| Feature | Generative AI | Predictive AI |
| Purpose | Creates new content. | Predicts future events. |
| Data Requirement | Requires large datasets. | Can work with smaller datasets. |
| Explainability | Often lacks transparency. | Relatively more interpretable. |
| Primary Use Cases | Content generation, creativity. | Decision-making, forecasting. |
Algorithmic Differences
- Generative AI uses deep learning models like GANs and transformers.
- Predictive AI employs statistical models and simpler machine learning algorithms like regression and decision trees.
Output
Generative AI creates new, unique outputs, while predictive AI provides insights into what’s likely to happen.
Also Read – Best Resources to Learn Generative AI for Salesforce Professionals
Choosing Between Generative and Predictive AI
When to Use Generative AI
- Need to create custom marketing visuals or ad copy.
- Want to develop synthetic data for testing or training.
- Require automated tools for content creation, like chatbots or code generators.
When to Use Predictive AI
- Forecasting product demand or sales trends.
- Identifying potential fraud in real-time.
- Personalizing user experiences based on behavioral predictions.
Factors to Consider
- Goal: Are you looking to create or predict?
- Data Availability: Do you have enough quality data for your chosen approach?
- Resources: Some AI systems require more computational power.
Real-World Use Cases
Generative AI in Action
- Marketing and Advertising: AI-powered tools like DALL-E and Adobe Firefly generate engaging visuals tailored to campaigns.
- Gaming: AI creates realistic environments and characters for immersive experiences.
Predictive AI in Action
- Retail: Helps optimize inventory and predict purchasing behavior.
- Healthcare: Assists in early disease detection through pattern analysis.
Also Read – Master Generative AI – A Must Skill in 2025
Conclusion
Generative AI and predictive AI represent two unique facets of artificial intelligence, each tailored to specific strengths. Generative AI specializes in crafting creative content, whereas predictive AI focuses on analyzing data to forecast trends and guide decision-making. Selecting the appropriate AI solution hinges on your goals and the resources at hand. Leveraging these advanced technologies can empower businesses to stay competitive and foster innovation in today’s AI-driven landscape.
For further insights, explore GetGenerative.ai.